Menopause is life for all women. It is the end of menstruation and fertile years. Menopause is something all women are bound to undergo but not all of them at the same time for all. The most basic and straightforward question all such women should be asking is: What is the average age of menopause, and how would it affect me?
Menopause awareness age is physical and emotional health. It prepares a woman for change, decreases worry, and makes choices that guard future wellness. This piece offers an overview of the average menopause age, how this fluctuates, symptoms to anticipate, and life skills to support during this phase of life.
What is Menopause
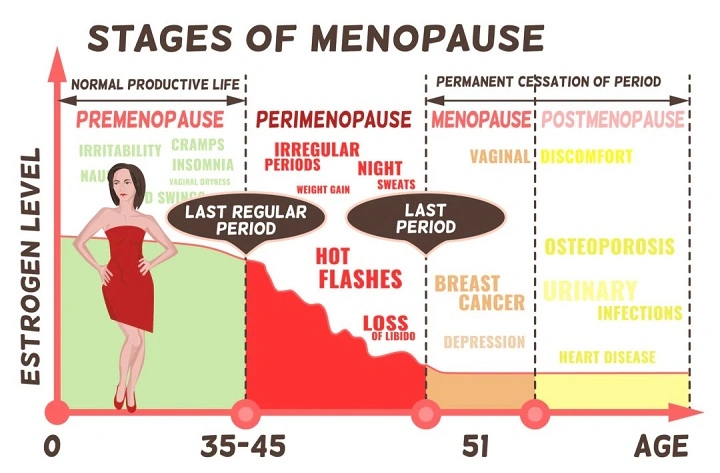
Menopause is a time when 12 consecutive months have been without menstrual bleeding. Menopause is the end of ovulation and decrease in reproductive hormones, i.e., progesterone and estrogen.
It is not usually sudden. Instead, it happens over a sequence of years, starting with perimenopause and leading to postmenopause.
Average Menopause Age
The majority of women undergo menopause when they are between 45 and 55 years of age. Menopause most often occurs to the majority of individuals at the midpoint of 51 years of age. Although that is the midpoint, it is due to a mixture of genes, living style, and health.
Menopause Age Divisions
- Early menopause: Less than 45
- Average menopause: 45-55
- Late menopause: Over 55
Not every woman goes through menopause at 40 years, but other women continue menstruating when they are over 50 years. Both are acceptable based on individual circumstances.
Conditions That Influence the Menopause Age
Genetics
Hereditary is one factor to check. If your mother and sisters experienced early or late menopause, then there are high chances that you will also go through the same.
Smoking is also a powerful risk factor for the development of menopause. Poor diet, alcohol use, and ongoing stress may also be involved. Good diet and moderate exercise, however, enhance even higher optimal hormone function.
Medical Conditions
- Surgery to the ovaries induces menopause immediately irrespective of age.
- Chemotherapy or irradiation can lead to premature ovarian failure too.
- Certain autoimmune conditions and thyroid disease can be accountable too.
Body Weight
- Underweight is accountable for inducing premature menopause.
- Obesity will hold back menopause at times.
- Endocrine homeostasis relies on the fat tissue that synthesizes estrogen.
Perimenopause and Effect on Menstrual Age at Menopause
There is a brief time leading up to menopause called perimenopause. It usually occurs in the mid to late 40s but may begin sooner.
Perimenopause Symptoms
- Irregular periods
- Good flushes and night sweats
- Disruption of sleep
- Mood changes
- Dry vagina
- Reduced fertility
Perimenopause lasts 4 to 8 years. How old the woman is when perimenopause begins is generally a fairly good estimate of when menopause begins.
Early Menopause
Early menopause is less than 45 years. Premature menopause is menopause less than 40 years.
Causes of Early Menopause
- Genetics
- Autoimmune disease
- Surgical removal of the ovaries
- Chemotherapy and radiation for cancer
- Smoking
Dangers to Health because of Early Menopause
- Bone density loss and risk of osteoporosis
- Risk of heart disease due to low estrogen
- Emotional problems, especially in those who want more children
Late Menopause
Over 55 years. Women with longer-duration have had the effect of estrogen for all these years.
Effects of Late Menopause on Health
- Lower risk of osteoporosis with estrogen reserved for so many years
- Slightly higher risk of endometrial and breast cancer
- In general, inherited tendency to occur later
Typical Symptoms
- Hot flashes
- Night sweats
- Sleep disruptions
- Mood swings
- Weight gain, especially around waist
- Dry vagina
- Painful intercourse
- Sex drive loss
- Memory or “foggy brain” issue
- Tangling hair and dry skin
Some women have terrible symptoms, and some never notice anything at all.
Health After Menopause
Age when menopause happens does make a difference because it means changes in health for many years. Estrogen maintains bones, heart, and metabolism. Once menopause has been achieved, new dangers are established for women.
Health Issues
- Osteoporosis: Unhealthier bones due to decreased estrogen
- Cardiovascular disease: Risk to the heart increases after menopause
- Weight gain: Metabolic change and fat redistribution
- Diabetes: Risk during hormonal change
Nutrition During Menopause
Symptoms are more readily managed on a healthful diet and long-term health is secured.
Foods to Emphasize
- Calcium foods: Milk, leafy greens, fortified plant milk
- Vitamin D sources: Sunlight, salmon, fortified foods
- Fiber foods: Oats, beans, fruits, vegetables
- Healthy fats: Olive oil, avocado, nuts, fatty fish
- Protein: Chicken, eggs, tofu, legumes
Foods to Limit
- Sweets and sweet drinks
- Very processed
- Excessive alcohol
- Salty snack foods
- Fried foods
Table: Menopause Diet at a Glance
| What to Eat | Why They Help |
| Leafy greens | Bone health, minerals |
| Salmon, sardines | Omega-3s, vitamin D |
| Beans and lentils | Fiber, protein |
| Nuts and seeds | Healthy fats, energy |
| Whole grains | Steady blood sugar |
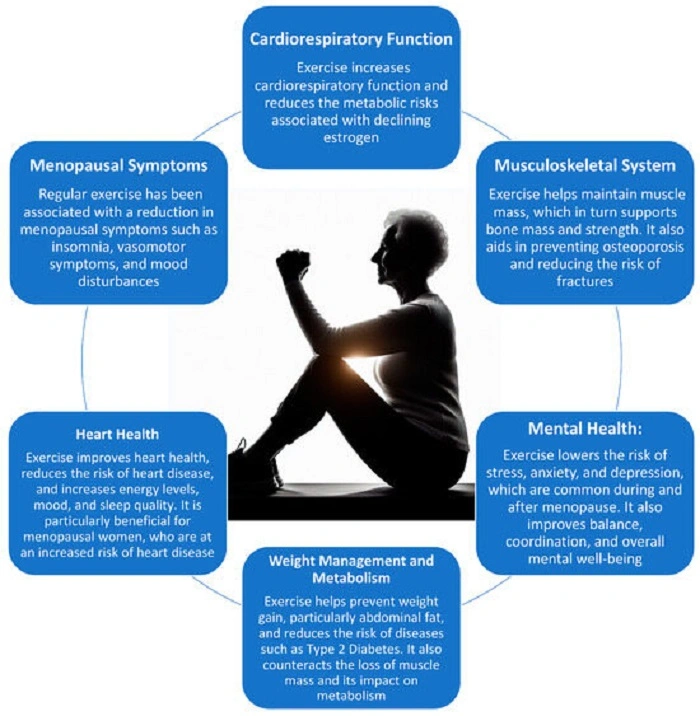
Exercise During and After Menopause

Physical activity every day maintains a healthy weight, builds bone density, and promotes good mental health.
Also Read: BBL Laser Treatment: Restore Your Skin’s Natural Glow
Best Types of Exercise
- Strength training: Maintains strong bones and muscles
- Cardio: Burns fat, strong heart
- Pilates and Yoga: Stretch and stress-reducing
- Walking: Easy to do and effective for overall well-being
Try to have at least 150 minutes of physical activity a week.
Sleep during Menopause
Insomnia is experienced by most women throughout menopausal life. Endocrine imbalance and night flushes interfere with sleep.
Sleep Improvement Tips
- Bedroom to be kept cool
- Avoid intake of caffeine at nighttime
- Establish soothing bedtime routine
- Less consumption of alcohol
- Night attire should be loose
Coping Skills
- Talk with supportive family and friends
- Join menopause support groups
- Seek counseling, as necessary, from experts
- Learn relaxation and mindfulness training
Medical Treatment
Physicians will treat with medication based on symptoms.
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT): Halts hot flashes, provides bone protection
- Non-hormonal medications: Suitable for women who can’t take HRT
- Local treatment: Vaginal estrogen creams to relieve dryness
- Bone density test: To avoid osteoporosis
Patient Experiences
- Sarah completed menopause at 48. She experienced hot flashes but found consolation in diet change and yoga.
- Maria experienced menopause at 54 years. She experienced tiny symptoms, but she tried nothing but calcium intake in a desperate attempt to protect herself against her bones.
- Linda experienced premature menopause at the age of 39 years after cancer treatment. She adhered to the doctor’s advice for bones and mental adjustment.
These are examples where menopausal age is uncertain but life and good care make it easy.
Menopause Age FAQs
What is the mean age of menopause?
The mean age of menopause is 45 to 55 years and mean age is 51.
Can menopause take place below the age of 40?
Yes, and it is premature menopause and can be on the grounds of genes, disease, or drug addiction.
Is lifestyle responsible for when menopause will take place?
Yes. Premature menopause takes place due to smoking, dietary regimen, and stress. Healthy way of living leads to delayed timing.
Is late menopause an evil thing?
It reduces the risk of osteoporosis but does have some cancer risk. Screening needs to be repeated.
How will I know I am in menopause?
If you have not had your period for 12 months and you are showing normal symptoms like hot flashes, then surely you are in menopause.
Conclusion
Menopause is life. Menopause comes usually when you are between 45 and 55 years old, but everyone is different. Premature menopause and late menopause come to some women. Time is decided by genes, lifestyle, and disease.
Education about menopause age prepares women. Menopause is under the control of diet, exercise, sleep, and medical care. Menopause is not a conclusion but rather a new start with space to grow, learn, and with more commitment to health.